Introduction:
In today's fast-paced and competitive business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, boost efficiency, and stay ahead of the curve. One critical aspect that plays a pivotal role in achieving these goals is Human Resources (HR) management. To meet the ever-evolving demands of HR functions, businesses are turning to revolutionary HRMS (Human Resource Management System) software solutions. This article explores how HRMS software can transform HR operations and drive success in business management.
Streamlining HR Processes:
Managing human resources involves a multitude of complex tasks, including employee data management, recruitment, onboarding, attendance tracking, payroll processing, performance evaluation, and more. HRMS software acts as a centralized platform that integrates all these functions, enabling streamlined and efficient management of HR processes. By automating routine tasks and eliminating manual paperwork, HRMS software frees up valuable time for HR professionals, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives and employee engagement.
Enhanced Employee Data Management:
One of the key features of HRMS software is its ability to efficiently store, organize, and retrieve employee data. From basic information such as personal details and job history to performance reviews and training records, HRMS software provides a secure and easily accessible database. This empowers HR teams to make informed decisions, track employee progress, identify skill gaps, and create targeted development plans. With accurate and up-to-date employee data, businesses can make better-informed decisions related to talent acquisition, succession planning, and resource allocation.
Efficient Recruitment and Onboarding:
Finding and attracting top talent is a critical aspect of business success. HRMS software streamlines the recruitment process by offering a range of tools, including applicant tracking systems (ATS), automated job postings, resume screening, and candidate evaluation. These features enable HR teams to identify the most qualified candidates efficiently, reducing the time and effort spent on manual applicant screening. Furthermore, HRMS software facilitates seamless onboarding, ensuring a smooth transition for new hires, with automated workflows for paperwork, training modules, and policy acknowledgments.
Streamlined Time and Attendance Management:
Tracking employee attendance, managing leave requests, and ensuring accurate payroll processing can be time-consuming and prone to errors. HRMS software provides comprehensive time and attendance management features, including online timesheets, automated leave tracking, and real-time reporting. This eliminates manual data entry, reduces payroll discrepancies, and increases transparency, allowing HR and payroll departments to function seamlessly. Additionally, employees can access their attendance records, request time off, and view their leave balances, promoting self-service and empowering staff members.
Insightful Analytics and Reporting:
Data-driven decision-making is vital for businesses to thrive. HRMS software offers robust analytics and reporting capabilities, providing HR professionals and management with valuable insights. These insights can include workforce demographics, performance trends, employee engagement levels, and turnover rates. By leveraging these analytics, organizations can identify patterns, detect potential issues, and develop proactive strategies to enhance employee satisfaction, retention, and overall productivity.
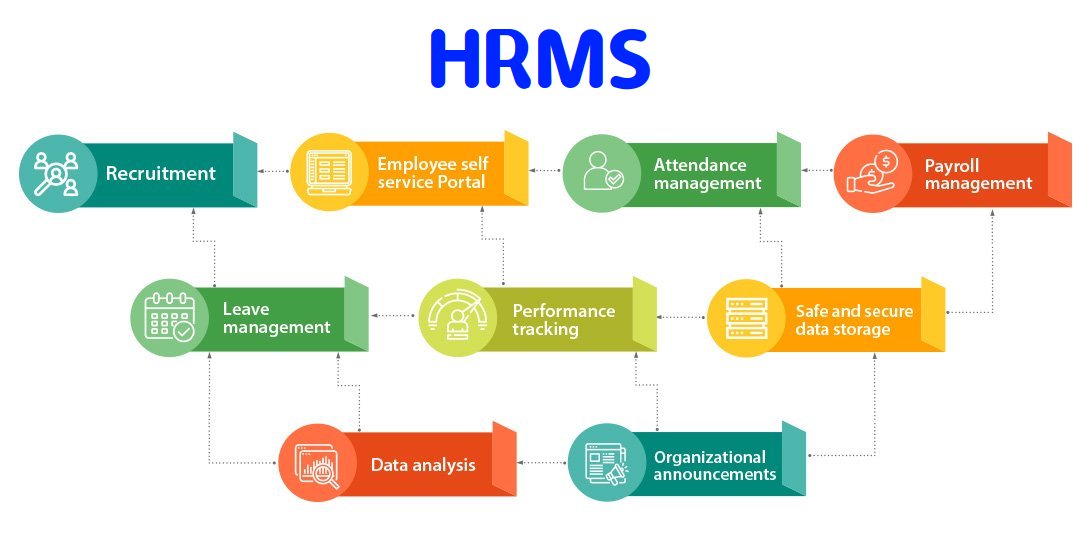
Modules included in "HRMS Software"
HRMS software typically encompasses a range of modules designed to address various aspects of human resource management. While the specific modules may vary depending on the software provider and the needs of the organization, here are some common modules included in HRMS software:
1. Employee Information Management: This module serves as a centralized database to store and manage employee information, including personal details, contact information, employment history, skills, and qualifications.
2. Recruitment and Applicant Tracking: This module assists in the end-to-end recruitment process, starting from job requisition creation, job posting, resume screening, interview scheduling, candidate evaluation, and selection. It may also include features for managing job boards, career portals, and candidate communication.
3. Onboarding: The onboarding module helps streamline the process of integrating new employees into the organization. It typically includes tasks such as document collection, policy acknowledgment, training management, and providing necessary resources for a smooth transition.
4. Time and Attendance Management: This module enables the tracking and management of employee attendance, leaves, and absences. It may include features like time tracking, shift scheduling, leave management, and integration with payroll systems for accurate calculation of wages.
5. Performance Management: Performance management modules facilitate the creation and management of performance goals, ongoing feedback, performance appraisals, and performance reviews. They often include features for setting objectives, tracking progress, and documenting performance-related discussions.
6. Training and Development: This module helps organizations manage employee training programs, track training needs, schedule and deliver training sessions, and monitor employee skill development. It may also include features for tracking certifications, compliance training, and employee self-service access to training resources.
7. Compensation and Benefits: This module handles the administration of employee compensation and benefits, including salary structures, allowances, bonuses, deductions, and benefits enrollment. It may also assist in managing payroll processes and generating payroll reports.
8. Employee Self-Service: Employee self-service modules empower employees to access and update their personal information, view pay stubs, submit leave requests, access company policies and documents, and communicate with HR through a self-service portal or mobile application.
9. Analytics and Reporting: This module provides HR professionals and management with data analytics and reporting tools to gain insights into workforce trends, turnover rates, performance metrics, and other HR-related metrics. It enables data-driven decision-making and strategic planning.
10. Compliance and HR Regulations: This module helps organizations ensure compliance with labor laws, industry regulations, and internal policies. It may include features for managing employee contracts, tracking expiration dates, and generating compliance reports.
These modules collectively form a comprehensive HRMS software suite that optimizes HR processes, enhances data management, improves employee engagement, and facilitates informed decision-making within an organization. The specific modules implemented can be tailored to meet the unique needs and priorities of each organization.
Conclusion:
Revolutionizing HR operations with HRMS software has become imperative for businesses striving for excellence in people management. By streamlining processes, enhancing employee data management, improving recruitment and onboarding, and providing valuable insights through analytics, HRMS software empowers organizations to optimize their human resources, drive business growth, and stay ahead of the competition. Embracing this technological advancement in business management is a strategic move towards a more efficient, productive, and engaged workforce, ultimately leading to long-term success.